-

DNA甲基化实验操作步骤
DNA甲基化检测第一步:引物设计在GenBank上找到待检基因启动子区的原始序列,输入到“MethPrimer”软件中,输入启动子序列,选择“Pick prim
-

Perfusion Culture of Mammalian Cells in a Microfluidic Channel with a Built-In Pillar Array
In vitro culture of mammalian cells is fundamental to various biological studies
-

Short- and Long-Term Cultivation of Embryonic and Neonatal Murine Keratinocytes
Studies using cultured cells allow one to dissect complex cellular mechanisms in
-

六种甲基化检测方法
1、全基因组重亚硫酸盐甲基化测序(WGBS)全基因组重亚硫酸盐甲基化测序(WGBS)可以在全基因组范围内精确的检测所有单个胞嘧啶碱基(C碱基)的甲基化水平,是D
-

Fluorescent Differential Display
Since their first introduction in 1992 (1 ,2 ), differential display (DD) and it
-
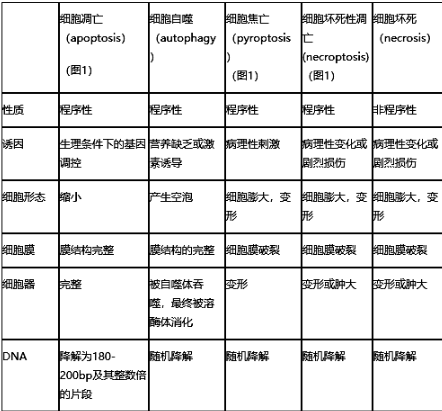
研究新热点之细胞焦亡
细胞焦亡(Pyroptosis)又称细胞炎性坏死,是一种程序性细胞死亡,表现为细胞不断胀大直至细胞膜破裂,导致细胞内容物的释放进而激活强烈的炎症反应。细胞焦亡是
-

Analysis of Janus Tyrosine Kinase Phosphorylation and Activation
Activation of Janus kinases (Jaks) occurs through autophosphorylation of key tyr
-

细胞焦亡的研究方法与检测方式
首先是细胞焦亡的特点:细胞焦亡发生时,细胞会发生肿胀,在细胞破裂之前,细胞上形成凸出物(图1,早期细胞焦亡),之后细胞膜上形成孔隙,使细胞膜失去完整性,释放内容
-

EMS Screens: From Mutagenesis to Screening and Mapping
The success of Drosophila as a genetic model organism is based on the efficient
-

Generation and Analysis of Biosensors to Measure Mechanical Forces Within Cells
The inability to measure mechanical forces within cells has been limiting our un
-

Confocal Microscopy of Live Xenopus Oocytes, Eggs, and Embryos
The use of the confocal microscope to study living Xenopus eggs affords the oppo
-

细胞焦亡在临床各领域的研究现状
首先是细胞焦亡与感染性疾病,也是我们在对细胞焦亡的研究中最简单也最广泛的。 在病原体感染时,适度的细胞焦亡可清除致病微生物,而过度的细胞焦亡在导致细胞死亡
-

In Vivo Detection of Protein-Protein Interaction in Plant Cells Using BRET
The emerging technique of bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET) allow
-

Quantitative Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization on Paraffin Embedded Tissue
Quantitative fluorescence in situ hybridization (Q-FISH) is a complex technique
-

Fluorescence Immunohistochemistry in Combination with Differential Interference Contrast Microscopy
We have developed a technique, using a combination of immunofluorescent staining

